/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
WiFi - WiFi.scanNetworks()
Description
Scans for available WiFi networks and returns the discovered number
Syntax
WiFi.scanNetworks();
Parameters
Returns
byte : number of discovered networks
Example
/*H********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
#include <WiFi.h>
char ssid[] = "yourNetwork"; // SSID (NAME) OF YOUR NETWORK
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
setup()
{
Serial.begin( 9600 );
int status = WiFi.begin( ssid );
if( status != WL_CONNECTED )
{
Serial.println( "Couldn't get a WiFi connection" );
while( true );
}
else
{
// if you are connected, scan for available WiFi networks and print
// the number discovered:
Serial.println( "** Scan Networks **" );
byte numSsid = WiFi.scanNetworks();
Serial.print( "Number of available WiFi networks discovered:" );
Serial.println( numSsid );
}
}
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
loop()
{}
Scan Class
This class is represented in Arduino WiFi library by scanNetworks() function.
Developers of esp8266 / Arduino core extend this functionality by additional
methods and properties.
Documentation of this class is divided into two parts. First covers functions to
scan for available networks. Second describes what information is collected
during scanning process and how to access it.
Scan for Networks
Scanning for networks takes hundreds of milliseconds to complete. This may be
done in a single run when we are triggering scan process, waiting for completion,
and providing result - all by a single function. Another option is to split this
into steps, each done by a separate function. This way we can execute other
tasks while scanning is in progress. This is called asynchronous scanning. Both
methods of scanning are documented below.
scanNetworks
Scan for available Wi-Fi networks in one run and return the number of networks
that has been discovered.
WiFi.scanNetworks()
There is on overload of this function that accepts two optional parameters to
provide extended functionality of asynchronous scanning as well as looking for
hidden networks.
WiFi.scanNetworks( async, show_hidden )
Both function parameters are of boolean type. They provide the folowing
functionality: * asysnc - if set to true then scanning will start in background
and function will exit without waiting for result. To check for result use
separate function scanComplete that is described below. * show_hidden - set it
to true to include in scan result networks with hidden SSID.
scanComplete
Check for result of asynchronous scanning.
WiFi.scanComplete()
On scan completion function returns the number of discovered networks.
If scan is not done, then returned value is < 0 as follows: * Scanning still in
progress: -1 * Scanning has not been triggered: -2
scanDelete
Delete the last scan result from memory.
WiFi.scanDelete()
scanNetworksAsync
Start scanning for available Wi-Fi networks. On completion execute another function.
WiFi.scanNetworksAsync( onComplete, show_hidden )
Function parameters:
* onComplete - the event handler executed when the scan is done
* show_hidden - optional boolean parameter, set it to true to scan for
hidden networks
/*H********************************************************************
* Example code:
**********************************************************************/
#include "ESP8266WiFi.h"
//************************* DEFINES ************************************
//************************* PROTOTYPES ************************************
void prinScanResult( int networksFound );
//************************* VARIABLES ************************************
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
setup()
{
Serial.begin( BAUD );
Serial.println();
WiFi.mode( WIFI_STA );
WiFi.disconnect();
delay( 100 );
WiFi.scanNetworksAsync( prinScanResult );
}
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
loop()
{}
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
prinScanResult( int networksFound )
{
int ndx;
Serial.printf( "%d network(s) found\n", networksFound);
for( ndx = 0; ndx < networksFound; ndx++)
{
Serial.printf( "%d: %s, Ch:%d (%ddBm) %s\n", ndx + 1
, WiFi.SSID(ndx).c_str() , WiFi.channel( ndx ), WiFi.RSSI( ndx )
, WiFi.encryptionType( ndx ) == ENC_TYPE_NONE ? "open" : "");
}
}
Example output:
5 network(s) found
1: Tech_D005107, Ch:6 (-72dBm)
2: HP-Print-A2-Photosmart 7520, Ch:6 (-79dBm)
3: ESP_0B09E3, Ch:9 (-89dBm) open
4: Hack-4-fun-net, Ch:9 (-91dBm)
5: UPC Wi-Free, Ch:11 (-79dBm)
Show Results
Functions below provide access to result of scanning. It does not matter if
scanning has been done in synchronous or asynchronous mode, scan results are
available using the same API.
Individual results are accessible by providing a `networkItem’ that identifies
the index (zero based) of discovered network.
SSID
Return the SSID of a network discovered during the scan.
WiFi.SSID( networkItem )
Returned SSID is of the String type. The networkItem is a zero based index of
network discovered during scan.
encryptionType
Return the encryption type of a network discovered during the scan.
WiFi.encryptionType( networkItem )
Function returns a number that encodes encryption type as follows:
* 5 : ENC_TYPE_WEP - WEP
* 2 : ENC_TYPE_TKIP - WPA / PSK
* 4 : ENC_TYPE_CCMP - WPA2 / PSK
* 7 : ENC_TYPE_NONE - open network
* 8 : ENC_TYPE_AUTO - WPA / WPA2 / PSK
The networkItem is a zero based index of network discovered during scan.
RSSI
Return the RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indication) of a network discovered
during the scan.
WiFi.RSSI( networkItem )
Returned RSSI is of the int32_t type. The networkItem is a zero based index of
network discovered during scan.
BSSID
Return the BSSID (Basic Service Set Identification) that is another name of MAC
address of a network discovered during the scan.
WiFi.BSSID( networkItem )
Function returns a pointer to the memory location (an uint8_t array with the
size of 6 elements) where the BSSID is saved.
If you do not like to pointers, then there is another version of this function
that returns a String.
WiFi.BSSIDstr( networkItem )
The networkItem is a zero based index of network discovered during scan.
channel
Return the channel of a network discovered during the scan.
WiFi.channel( networkItem )
Returned channel is of the int32_t type. The networkItem is a zero based index
of network discovered during scan.
isHidden
Return information if a network discovered during the scan is hidden or not.
WiFi.isHidden( networkItem )
Returned value if the boolean type, and true means that network is hidden. The
networkItem is a zero based index of network discovered during scan.
getNetworkInfo
Return all the network information discussed in this chapter above in a single
function call.
WiFi.getNetworkInfo( networkItem, &ssid, &encryptionType
, &RSSI, *&BSSID, &channel, &isHidden )
The networkItem is a zero based index of network discovered during scan. All
other input parameters are passed to function by reference. Therefore they will
be updated with actual values retrieved for particular networkItem. The function
itself returns boolean true or false to confirm if information retrieval was
successful or not.
Example code:
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
int n = WiFi.scanNetworks( false, true );
String ssid;
uint8_t encryptionType;
int32_t RSSI;
uint8_t* BSSID;
int32_t channel;
bool isHidden;
for( int i = 0; i < n; i++ )
{
WiFi.getNetworkInfo( i, ssid, encryptionType, RSSI, BSSID, channel
, isHidden);
Serial.printf( "%d: %s, Ch:%d (%ddBm) %s %s\n", i + 1, ssid.c_str()
, channel, RSSI, encryptionType == ENC_TYPE_NONE ? "open" : ""
, isHidden ? "hidden" : "");
}
Example output:
6 network(s) found
1: Tech_D005107, Ch:6 (-72dBm)
2: HP-Print-A2-Photosmart 7520, Ch:6 (-79dBm)
3: ESP_0B09E3, Ch:9 (-89dBm) open
4: Hack-4-fun-net, Ch:9 (-91dBm)
5: , Ch:11 (-77dBm) hidden
6: UPC Wi-Free, Ch:11 (-79dBm)
For code samples please refer to separate section with examples dedicated
specifically to the Scan Class.
getScanInfoByIndex
Similar to the getNetworkInfo, but instead returns a pointer to the Nth bss_info
structure which is internally used by the NONOS SDK.
WiFi.getScanInfoByIndex( networkItem )
The networkItem is a zero based index of network discovered during scan.
Function will return nullptr when networkItem is greater than the number of
networks in the scan result or when there are no scan results available.
auto n = WiFi.scanNetworks( false, true );
if( n <= 0 )
{
// SCAN FAILED OR THERE ARE NO RESULTS
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
const auto* info = WiFi.getScanInfoByIndex(i)
// ... use the raw data from the bss_info structure ...
}
******************************************************************
Scan Networks
Displays all WiFi networks in range.
LAST REVISION: 10/05/2022, 08:00 AM
This example scans for 802.11b/g networks with the Arduino WiFi shield. Your
Arduino Software (IDE) serial monitor will print out information about the board
and the networks it can see. It will not connect to a network.
Hardware Required
Arduino WiFi Shield
Shield-compatible Arduino board
Circuit
The WiFi shield uses pins 10, 11, 12, and 13 for the SPI connection to the
HDG104 module. Digital pin 4 is used to control the chip select pin on the SD
card.
Open your serial monitor to view the networks the WiFi shield can see. The
shield may not see as many networks as your computer.
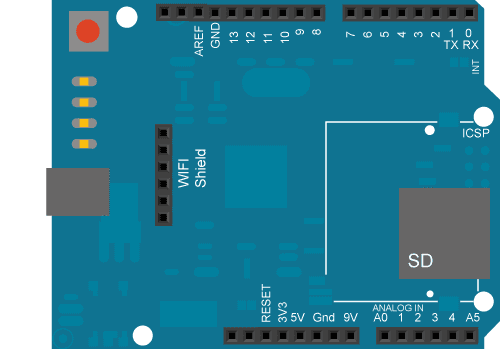 WiFiShield bb
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing
project page
In the above image, the board would be stacked below the WiFi shield.
WiFiShield bb
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing
project page
In the above image, the board would be stacked below the WiFi shield.
Code
/*H*******************************************************
This example prints the Wifi shield's MAC address, and
scans for available Wifi networks using the Wifi shield.
Every ten seconds, it scans again. It doesn't actually
connect to any network, so no encryption scheme is specified.
Circuit: * WiFi shield attached
created 13 July 2010 by dlf (Metodo2 srl)
modified 21 Junn 2012 by Tom Igoe and Jaymes Dec
********************************************************/
#include
#include
//************************* DEFINES ************************************
//************************* PROTOTYPES ************************************
//************************* VARIABLES ************************************
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
setup()
{
//Initialize serial and wait for port to open:
Serial.begin( BAUD );
while( !Serial )
{
;// WAIT FOR SERIAL PORT TO CONNECT. nEEDED FOR NATIVE USB PORT ONLY
}
// check for the presence of the shield:
if( WiFi.status() == WL_NO_SHIELD )
{
Serial.println("WiFi shield not present");
while( true ); // DON'T CONTINUE
}
String fv = WiFi.firmwareVersion();
if( fv != "1.1.0" )
Serial.println("Please upgrade the firmware");
printMacAddress(); // PRINT WiFi MAC ADDRESS
}
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
loop()
{
Serial.println( "Scanning available networks...");
listNetworks(); // SCAN FOR EXISTING NETWORKS
delay( 10000 );
}
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
printMacAddress()
{
byte mac[6]; // MAC ADDRESS OF YOUR Wifi SHIELD
WiFi.macAddress( mac ); // PRINT YOUR MAC ADDRESS
Serial.print( "MAC: ");
Serial.print( mac[5], HEX );
Serial.print( ":" );
Serial.print( mac[4], HEX );
Serial.print( ":" );
Serial.print( mac[3], HEX );
Serial.print( ":" );
Serial.print( mac[2], HEX );
Serial.print( ":" );
Serial.print( mac[1], HEX );
Serial.print( ":" );
Serial.println( mac[0], HEX );
}
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
listNetworks()
{
Serial.println( "** Scan Networks **");
int numSsid = WiFi.scanNetworks(); // SCAN FOR NEARBY NETWORKS
if (numSsid == -1)
{
Serial.println( "Couldn't get a wifi connection");
while( true );
}
Serial.print( "number of available networks:");
Serial.println( numSsid ); // PRINT LIST OF NETWORKS SEEN
for( int thisNet = 0; thisNet < numSsid; thisNet++ )
{ // PRINT NETWORK NUMBER AND NAME FOR EACH NETWORK FOUND
Serial.print( thisNet );
Serial.print( ") " );
Serial.print( WiFi.SSID( thisNet ) );
Serial.print( "\tSignal: " );
Serial.print( WiFi.RSSI( thisNet ) );
Serial.print( " dBm" );
Serial.print( "\tEncryption: " );
printEncryptionType( WiFi.encryptionType( thisNet ) );
}
}
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
printEncryptionType( int thisType )
{
switch( thisType ) // READ ENCRYPTION TYPE AND PRINT OUT NAME
{
case ENC_TYPE_WEP:
Serial.println("WEP");
break;
case ENC_TYPE_TKIP:
Serial.println("WPA");
break;
case ENC_TYPE_CCMP:
Serial.println("WPA2");
break;
case ENC_TYPE_NONE:
Serial.println("None");
break;
case ENC_TYPE_AUTO:
Serial.println("Auto");
break;
}
}
Another Example
/*H*******************************************************
THIS EXAMPLE PRINTS WiFi SHIELD'S MAC ADDRESS, AND SCANS FOR AVAILABLE WiFi
NETWORKS USING WiFi SHIELD. EVERY TEN SECONDS, IT SCANS AGAIN. IT DOESN'T
ACTUALLY CONNECT TO ANY NETWORK, SO NO ENCRYPTION SCHEME IS SPECIFIED.
Circuit: * WiFi SHIELD ATTACHED
created 13 July 2010 by dlf (Metodo2 srl)
modified 21 Junn 2012 by Tom Igoe and Jaymes Dec
********************************************************/
#include
#include
//************************* DEFINES ************************************
//************************* PROTOTYPES ************************************
void printMacAddress();
void listNetworks();
void printEncryptionType( int thisType );
//************************* VARIABLES ************************************
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
setup()
{
Serial.begin( BAUD );
while( !Serial )
{
; // WAIT FOR SERIAL PORT TO CONNECT. NEEDED FOR NATIVE USB PORT ONLY
}
if( WiFi.status() == WL_NO_SHIELD ) // CHECK FOR PRESENCE OF SHIELD
{
Serial.println( "WiFi shield not present" );
while( true ); // DON'T CONTINUE
}
String fv = WiFi.firmwareVersion();
if( fv != "1.1.0" )
Serial.println( "Please upgrade the firmware" );
printMacAddress(); // PRINT WiFi MAC ADDRESS
}
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
loop()
{
// SCAN FOR EXISTING NETWORKS
Serial.println( "Scanning available networks..." );
listNetworks();
delay( 10000 );
}
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
printMacAddress()
{
byte mac[6]; // MAC ADDRESS OF WiFi SHIELD
WiFi.macAddress( mac ); // PRINT MAC ADDRESS
Serial.print( "MAC: " );
Serial.print( mac[5], HEX );
Serial.print( ":" );
Serial.print( mac[4], HEX );
Serial.print( ":" );
Serial.print( mac[3], HEX );
Serial.print( ":" );
Serial.print( mac[2], HEX );
Serial.print( ":" );
Serial.print( mac[1], HEX );
Serial.print( ":" );
Serial.println( mac[0], HEX );
}
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
listNetworks()
{
int thisNet;
Serial.println( "** Scan Networks **" ); // SCAN FOR NEARBY NETWORKS
int numSsid = WiFi.scanNetworks();
if( numSsid == -1)
{
Serial.println( "Couldn't get a WiFi connection" );
while( true );
}
Serial.print( "number of available networks:" );
Serial.println( numSsid ); // PRINT LIST OF NETWORKS SEEN
for( thisNet = 0; thisNet < numSsid; thisNet++ )
{ // PRINT NETWORK NUMBER AND NAME FOR EACH NETWORK FOUND
Serial.print( thisNet );
Serial.print( ") " );
Serial.print( WiFi.SSID( thisNet ) );
Serial.print( "\tSignal: " );
Serial.print( WiFi.RSSI( thisNet ) );
Serial.print( " dBm" );
Serial.print( "\tEncryption: " );
printEncryptionType( WiFi.encryptionType( thisNet ) );
}
}
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
printEncryptionType( int thisType )
{
switch( thisType ) // READ ENCRYPTION TYPE AND PRINT OUT NAME
{
case ENC_TYPE_WEP:
Serial.println ("WEP" );
break;
case ENC_TYPE_TKIP:
Serial.println( "WPA" );
break;
case ENC_TYPE_CCMP:
Serial.println( "WPA2" );
break;
case ENC_TYPE_NONE:
Serial.println( "None") ;
break;
case ENC_TYPE_AUTO:
Serial.println( "Auto" );
break;
}
}
 WiFiShield bb
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing
project page
In the above image, the board would be stacked below the WiFi shield.
WiFiShield bb
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing
project page
In the above image, the board would be stacked below the WiFi shield.