Binary Synchronous Communication (BISYNC) is basically a character or byte-oriented form of communication which means that the groups of bits or bytes are the important elements of transmission rather than a stream of bits. BISYNC was established or originated by IBM in 1960’s. It generally includes characters and procedures for simply controlling the establishment or development of a valid connection and transmission of data. It is a half-duplex link protocol that has replaced the Synchronous transmit-receive (STR) protocol usually used with second-generation computers.
It is also known as Basic Mode Protocol that is required for transmission of bit-oriented data basically known as transparent mode. It is also being replaced largely by much more efficient protocol of IBM i.e. Synchronous Data Link Control (SDLC) that is usually under SAN (Systems Network Architecture). BSC or BISYNC also used to describe various types of data packets as given below :
Types of Frames :
There are basically two types of BSC or BISYNC frames as shown below :
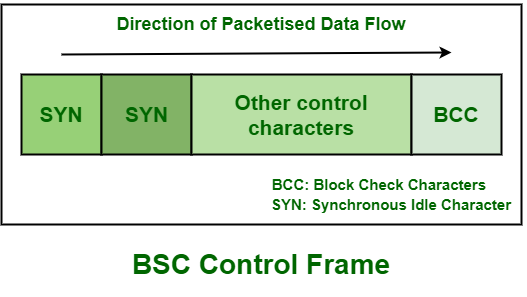
1. Control Frame :
These
frames are basically required for exchange of information or data among
devices to develop or obtain initial connection, provide flow and error
control, and also disconnect the devices when the session is completely
over. This frame does not contain any header.

2. Data Frame :
These
frames are basically required to carry user data. It is also used to
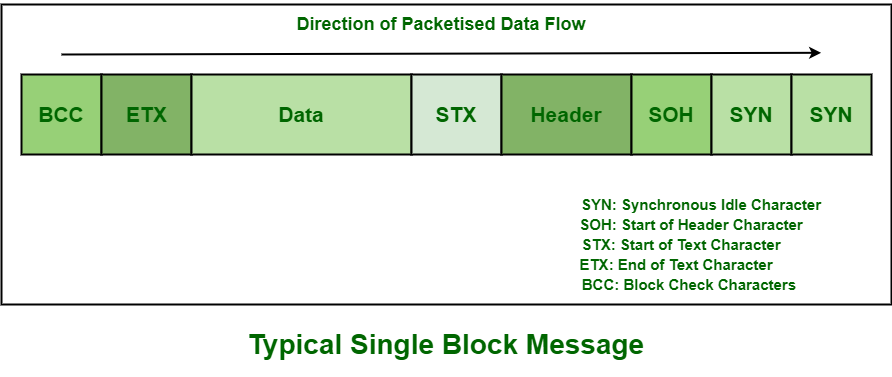
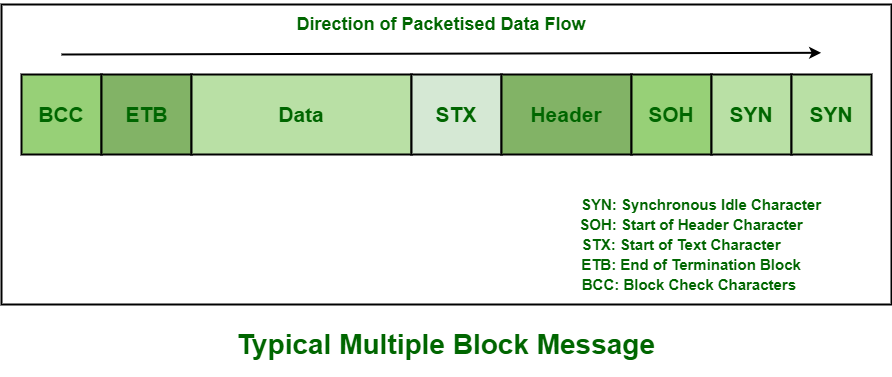
show the direction of data transfer. BISYNC allows for two types of
block messages i.e. Single-block and multiple-block message. The only
difference in both of these blocks is that data in single-block messages
would be terminated with ETB (End of Transmission Block) character
rather than an ETX (End of Text) character.
Single Block Data Frame :
Multiple Block Data Frame:
Control Characters for BISYNC :
Some of the Standard Control Protocols that are used in BISYNC frames are
given below :
| Character | ASCII Code | Function |
|---|---|---|
| ACK 0 | DLE 0 | Good even frame received or ready to receive |
| ACK 1 | DLE 1 | Good odd frame received |
| DLE | DLE | Data Transparency Marker |
| EOT | EOT | Sender Terminating |
| ETX | ETX | End of Text in message |
| ETB | ETB | End of Transmission block: ACK required |
| SOH | SOH | Header Information Begins |
| STX | STX | Text Begins |
| SYN | SYN | Alert receiver to the incoming frame |