Capacitance and Charge

| Capacitors store electrical energy on their plates in the form of an electrical charge |
 capacitance and charge on a capacitor
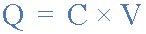
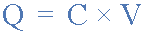
Where: Q (Charge, in Coulombs) = C (Capacitance, in Farads) x V (Voltage,
in
Volts)
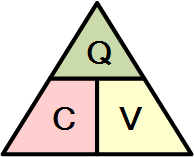
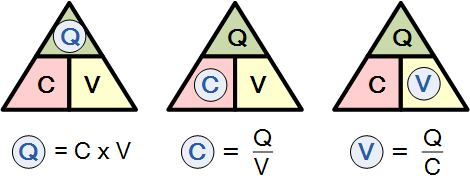
It is sometimes easier to remember this relationship by using pictures.
Here
the three quantities of Q, C and V have been superimposed into a triangle
giving charge at the top with capacitance and voltage at the bottom. This
arrangement represents the actual position of each quantity in the
Capacitor
Charge formulas.
capacitance and charge on a capacitor
Where: Q (Charge, in Coulombs) = C (Capacitance, in Farads) x V (Voltage,
in
Volts)
It is sometimes easier to remember this relationship by using pictures.
Here
the three quantities of Q, C and V have been superimposed into a triangle
giving charge at the top with capacitance and voltage at the bottom. This
arrangement represents the actual position of each quantity in the
Capacitor
Charge formulas.
 capacitor charge
and transposing the above equation gives us the following combinations of
the same equation:
capacitor charge
and transposing the above equation gives us the following combinations of
the same equation:
 capacitor charge equation
Units of: Q measured in Coulombs, V in volts and C in Farads.
Then from above we can define the unit of Capacitance as being a constant
of
proportionality being equal to the coulomb/volt which is also called a
Farad, unit F.
As capacitance represents the capacitors ability (capacity) to store an
electrical charge on its plates we can define one Farad as the
“capacitance of a capacitor which requires a charge of one coulomb to
establish a potential difference of one volt between its plates” as
firstly described by Michael Faraday. So the larger the capacitance, the
higher is the amount of charge stored on a capacitor for the same amount of
voltage.
The ability of a capacitor to store a charge on its conductive plates gives
it its Capacitance value. Capacitance can also be determined from the
dimensions or area, A of the plates and the properties of the dielectric
material between the plates. A measure of the dielectric material is given
by the permittivity, ( ε ), or the dielectric constant. So another way of
expressing the capacitance of a capacitor is:
capacitor charge equation
Units of: Q measured in Coulombs, V in volts and C in Farads.
Then from above we can define the unit of Capacitance as being a constant
of
proportionality being equal to the coulomb/volt which is also called a
Farad, unit F.
As capacitance represents the capacitors ability (capacity) to store an
electrical charge on its plates we can define one Farad as the
“capacitance of a capacitor which requires a charge of one coulomb to
establish a potential difference of one volt between its plates” as
firstly described by Michael Faraday. So the larger the capacitance, the
higher is the amount of charge stored on a capacitor for the same amount of
voltage.
The ability of a capacitor to store a charge on its conductive plates gives
it its Capacitance value. Capacitance can also be determined from the
dimensions or area, A of the plates and the properties of the dielectric
material between the plates. A measure of the dielectric material is given
by the permittivity, ( ε ), or the dielectric constant. So another way of
expressing the capacitance of a capacitor is:
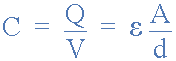 air dielectric capacitance
Capacitor with a Solid as its dielectric
air dielectric capacitance
Capacitor with a Solid as its dielectric
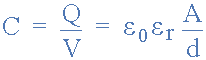 solid dielectric capacitance
Where A is the area of the plates in square metres, m2 with the larger the
area, the more charge the capacitor can store. d is the distance or
separation between the two plates.
The smaller is this distance, the higher is the ability of the plates to
store charge, since the -ve charge on the -Q charged plate has a greater
effect on the +Q charged plate, resulting in more electrons being repelled
off of the +Q charged plate, and thus increasing the overall charge.
ε0 (epsilon) is the value of the permittivity for air which is 8.854 x 10
-12 F/m, and εr is the permittivity of the dielectric medium used between
the two plates.
solid dielectric capacitance
Where A is the area of the plates in square metres, m2 with the larger the
area, the more charge the capacitor can store. d is the distance or
separation between the two plates.
The smaller is this distance, the higher is the ability of the plates to
store charge, since the -ve charge on the -Q charged plate has a greater
effect on the +Q charged plate, resulting in more electrons being repelled
off of the +Q charged plate, and thus increasing the overall charge.
ε0 (epsilon) is the value of the permittivity for air which is 8.854 x 10
-12 F/m, and εr is the permittivity of the dielectric medium used between
the two plates.
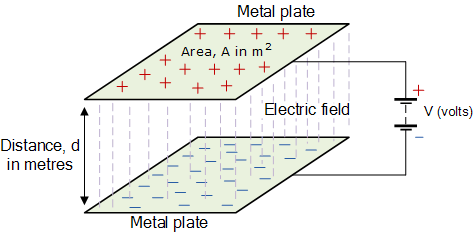 parallel plate capacitor
We have said previously that the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor
is proportional to the surface area A and inversely proportional to the
distance, d between the two plates and this is true for dielectric medium
of
air. However, the capacitance value of a capacitor can be increased by
inserting a solid medium in between the conductive plates which has a
dielectric constant greater than that of air.
Typical values of epsilon ε for various commonly used dielectric materials
are: Air = 1.0, Paper = 2.5 – 3.5, Glass = 3 – 10, Mica = 5 – 7 etc.
The factor by which the dielectric material, or insulator, increases the
capacitance of the capacitor compared to air is known as the Dielectric
Constant, (k). “k” is the ratio of the permittivity of the dielectric
medium being used to the permittivity of free space otherwise known as a
vacuum.
Therefore, all the capacitance values are related to the permittivity of
vacuum. A dielectric material with a high dielectric constant is a better
insulator than a dielectric material with a lower dielectric constant.
Dielectric constant is a dimensionless quantity since it is relative to
free
space.
parallel plate capacitor
We have said previously that the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor
is proportional to the surface area A and inversely proportional to the
distance, d between the two plates and this is true for dielectric medium
of
air. However, the capacitance value of a capacitor can be increased by
inserting a solid medium in between the conductive plates which has a
dielectric constant greater than that of air.
Typical values of epsilon ε for various commonly used dielectric materials
are: Air = 1.0, Paper = 2.5 – 3.5, Glass = 3 – 10, Mica = 5 – 7 etc.
The factor by which the dielectric material, or insulator, increases the
capacitance of the capacitor compared to air is known as the Dielectric
Constant, (k). “k” is the ratio of the permittivity of the dielectric
medium being used to the permittivity of free space otherwise known as a
vacuum.
Therefore, all the capacitance values are related to the permittivity of
vacuum. A dielectric material with a high dielectric constant is a better
insulator than a dielectric material with a lower dielectric constant.
Dielectric constant is a dimensionless quantity since it is relative to
free
space.
 capacitance value
then the value of the capacitor is 44pF.
capacitance value
then the value of the capacitor is 44pF.
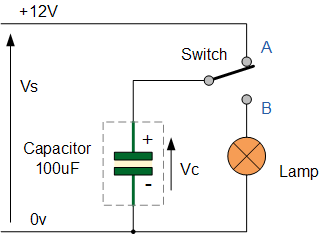 capacitor circuit
Assume that the capacitor is fully discharged and the switch connected to
the capacitor has just been moved to position A. The voltage across the
100uf capacitor is zero at this point and a charging current ( i ) begins to
flow charging up the capacitor exponentially until the voltage across the
plates is very nearly equal to the 12v supply voltage. After 5 time
constants the current becomes a trickle charge and the capacitor is said to
be “fully-charged”. Then, VC = VS = 12 volts.
Once the capacitor is “fully-charged” in theory it will maintain its
state of voltage charge even when the supply voltage has been disconnected
as they act as a sort of temporary storage device. However, while this may
be true of an “ideal” capacitor, a real capacitor will slowly discharge
itself over a long period of time due to the internal leakage currents
flowing through the dielectric.
This is an important point to remember as large value capacitors connected
across high voltage supplies can still maintain a significant amount of
charge even when the supply voltage is switched “OFF”.
If the switch was disconnected at this point, the capacitor would maintain
its charge indefinitely, but due to internal leakage currents flowing across
its dielectric the capacitor would very slowly begin to discharge itself as
the electrons passed through the dielectric. The time taken for the
capacitor to discharge down to 37% of its supply voltage is known as its
Time Constant.
If the switch is now moved from position A to position B, the fully charged
capacitor would start to discharge through the lamp now connected across it,
illuminating the lamp until the capacitor was fully discharged as the
element of the lamp has a resistive value.
The brightness of the lamp and the duration of illumination would ultimately
depend upon the capacitance value of the capacitor and the resistance of the
lamp (t = R*C). The larger the value of the capacitor the brighter and
longer will be the illumination of the lamp as it could store more charge.
capacitor circuit
Assume that the capacitor is fully discharged and the switch connected to
the capacitor has just been moved to position A. The voltage across the
100uf capacitor is zero at this point and a charging current ( i ) begins to
flow charging up the capacitor exponentially until the voltage across the
plates is very nearly equal to the 12v supply voltage. After 5 time
constants the current becomes a trickle charge and the capacitor is said to
be “fully-charged”. Then, VC = VS = 12 volts.
Once the capacitor is “fully-charged” in theory it will maintain its
state of voltage charge even when the supply voltage has been disconnected
as they act as a sort of temporary storage device. However, while this may
be true of an “ideal” capacitor, a real capacitor will slowly discharge
itself over a long period of time due to the internal leakage currents
flowing through the dielectric.
This is an important point to remember as large value capacitors connected
across high voltage supplies can still maintain a significant amount of
charge even when the supply voltage is switched “OFF”.
If the switch was disconnected at this point, the capacitor would maintain
its charge indefinitely, but due to internal leakage currents flowing across
its dielectric the capacitor would very slowly begin to discharge itself as
the electrons passed through the dielectric. The time taken for the
capacitor to discharge down to 37% of its supply voltage is known as its
Time Constant.
If the switch is now moved from position A to position B, the fully charged
capacitor would start to discharge through the lamp now connected across it,
illuminating the lamp until the capacitor was fully discharged as the
element of the lamp has a resistive value.
The brightness of the lamp and the duration of illumination would ultimately
depend upon the capacitance value of the capacitor and the resistance of the
lamp (t = R*C). The larger the value of the capacitor the brighter and
longer will be the illumination of the lamp as it could store more charge.
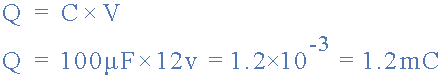 capacitance and charge equation
then the charge on the capacitor is 1.2 millicoulombs.
capacitance and charge equation
then the charge on the capacitor is 1.2 millicoulombs.
As the voltage across the plates increases (or decreases) over time, the current flowing through the capacitance deposits (or removes) charge from its plates with the amount of charge being proportional to the applied voltage. Then both the current and voltage applied to a capacitance are functions of time and are denoted by the symbols, i(t) and v(t). However, from the above equation we can also see that if the voltage remains constant, the charge will become constant and therefore the current will be zero!. In other words, no change in voltage, no movement of charge and no flow of current. This is why a capacitor appears to “block” current flow when connected to a steady state DC voltage.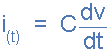
current and voltage of a capacitor current through a capacitor
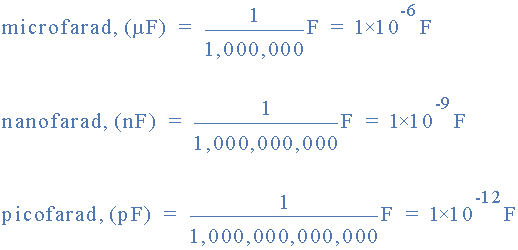 capacitance prefixes
Convert the following capacitance values:
capacitance prefixes
Convert the following capacitance values:
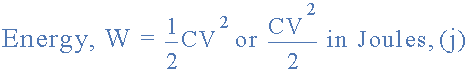 so the energy stored in the 100uF capacitor circuit above is calculated as:
so the energy stored in the 100uF capacitor circuit above is calculated as:
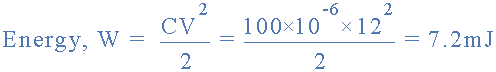 energy in a capacitor
The next tutorial in our section about Capacitors, we look at Capacitor
Colour Codes and see the different ways that the capacitance and voltage
values of the capacitor are marked onto its body.
energy in a capacitor
The next tutorial in our section about Capacitors, we look at Capacitor
Colour Codes and see the different ways that the capacitance and voltage
values of the capacitor are marked onto its body.