Pre-Info 2 This is a summary of the article: https://artiya4u.medium.com/formatting-usb-flash-drive-for-macos-on-ubuntu-f445c6b052bb Formatting USB flash drive for macOS on Ubuntu. From: https://superuser.com/questions/1758221/how-to-format-a-usb-stick-with-gparted-under-linux-so-it-shows-up-on-a-mac
- Open GParted and select your flash drive.
- Right-click and select "Unmount" on all its partitions.
- Select menu Device > Create Partition Table…
- Choose "gpt" and click "Apply"
- Right-click on the unallocated space, select "New" and "fat32"
- Click "Add"
- Click the checkbox on top to apply all operations and wait.
- Remove and re-insert to access the new drive.
How to Format USB Drive on Linux? | 3 Methods A USB is a practical accessory that provides a wide range of allocation and customization choices. To utilize its potential, one must understand how it operates. We frequently need to update a file system for better system flexibility or erase data for any particular purpose. We need formatting at times like this. But many people view it as a tiresome process they don't want to encounter. So, in this article, we'll walk you through the process of formatting your USB drive step by step. The "Discs" program or the terminal can be used for this. So let's get started without further ado. Many people view USB formatting as a taxing operation. There are various things to watch out for when it comes to windows. Linux, though, makes it far simpler. Don't worry; once you've read this tutorial, you'll be able to format your drive without any problems at all.
In Linux Format USB Drive Can Be Done in 3 Ways: Luckily, formatting a flash drive is simple and quick using the 3 techniques listed below: With USB devices, file sharing between platforms is really simple. They can also be used to create live Linux installation mediums. Using dedicated flash drives is simple because they are plug-and-play devices. However, there may be times when you want to format your USB drive under Linux. In linux format USB is required (for instance, while changing the file system or deleting data) on occasion. However, a lot of Linux users are reluctant to begin the formatting procedure because they believe it will be difficult or take a long time.
Format USB Drive with the Linux Terminal Formatting a USB device is easy if you already know about the terminal. Many command-line tools can be used for this process, as may be seen in the list below. Locate the USB Drive Before you can format your USB drive, you must locate the appropriate device. Use the lsblk command to find out what your drive's device name is. After attaching your USB to the desired port, give the command: lsblk The essential device can be determined by looking at the size. It should be something along the lines of /dev/sdX , where X is one of a, b, c, or something else.
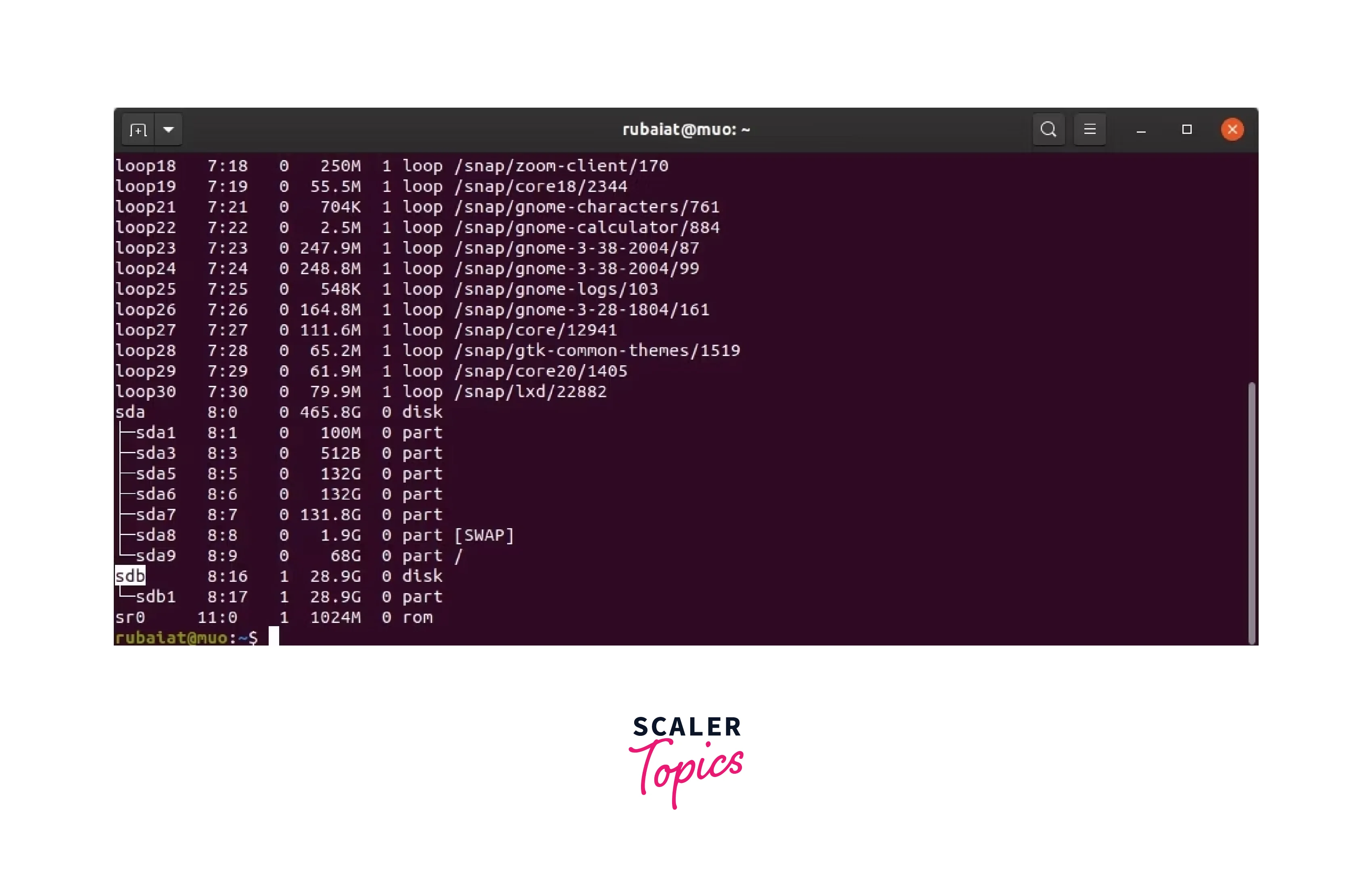 locating usb drive
Remove the USB
The USB partition should be removed than. As the remainder of this tutorial,
we'll assume that the device's name is /dev/sdb and that its disc partition
is /dev/sdb1.
sudo umount /dev/sdb1
With the umount command, the device is unmounted. Now that you're ready,
format the USB.
Format the USB Drive
By dismounting the device, you can continue to format it with a new file
system. Make cautious to backup any crucial files because you will lose
access to them after completing this step.
sudo mkfs.vfat -F 32 /dev/sdb1
With the aforementioned command, you can format your USB drive using the
popular FAT32 file system. However, you can choose an alternative file system
like NTFS or exFAT.
locating usb drive
Remove the USB
The USB partition should be removed than. As the remainder of this tutorial,
we'll assume that the device's name is /dev/sdb and that its disc partition
is /dev/sdb1.
sudo umount /dev/sdb1
With the umount command, the device is unmounted. Now that you're ready,
format the USB.
Format the USB Drive
By dismounting the device, you can continue to format it with a new file
system. Make cautious to backup any crucial files because you will lose
access to them after completing this step.
sudo mkfs.vfat -F 32 /dev/sdb1
With the aforementioned command, you can format your USB drive using the
popular FAT32 file system. However, you can choose an alternative file system
like NTFS or exFAT.
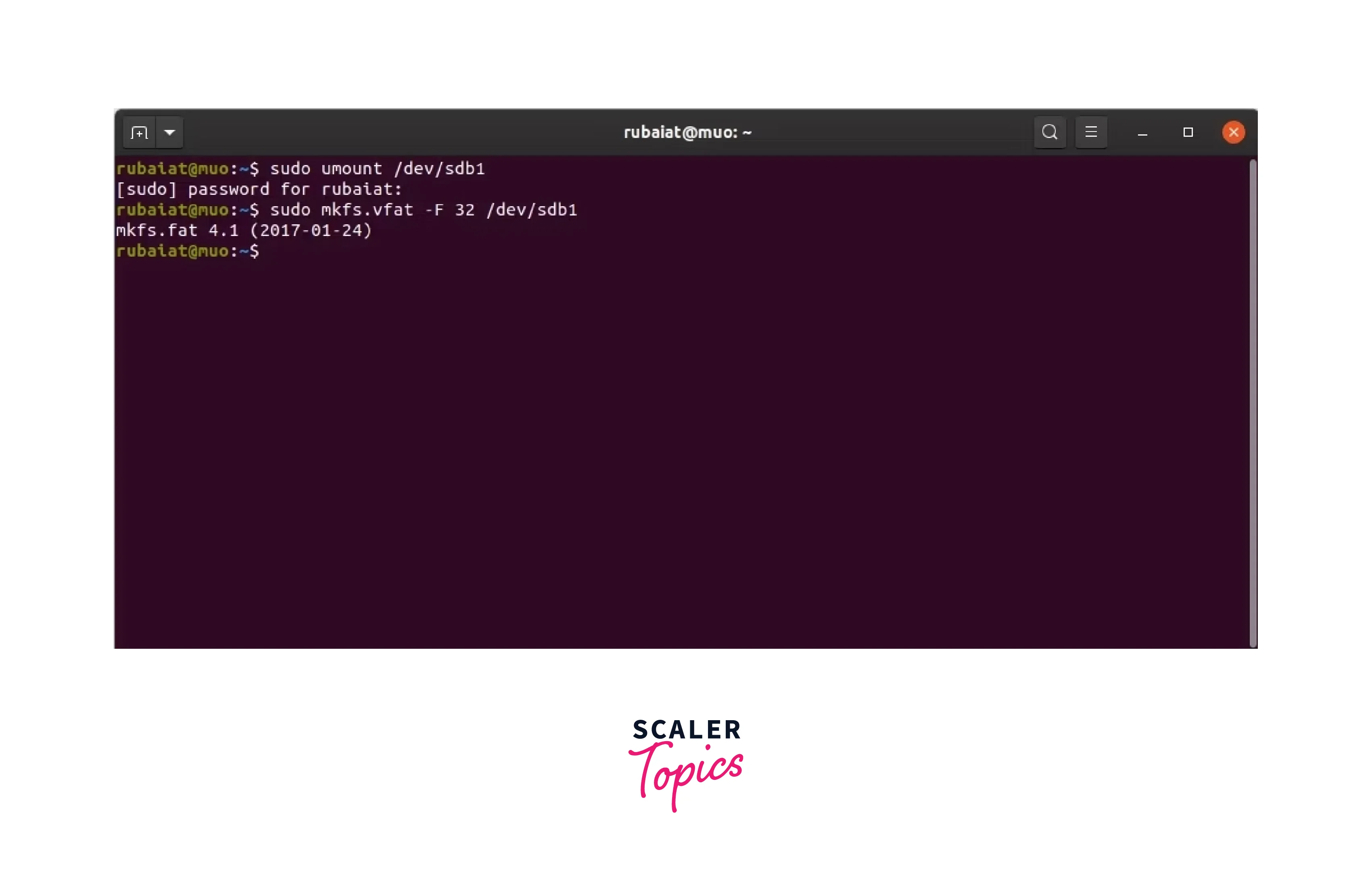 format usb drive
To give your gadget a name, use the -n option.
sudo mkfs.vfat -F 32 -n 'live-usb' /dev/sdb1
format usb drive
To give your gadget a name, use the -n option.
sudo mkfs.vfat -F 32 -n 'live-usb' /dev/sdb1
Format USB Drive with Disks Utility In linux format USB can be done using disks. Most of popular Linux distributions come pre-installed with a disc manager. For instance, Ubuntu comes with the GNOME Disc Utility—Disks. Linux users may easily format USB drives with this utility. To format yours, follow the instructions below. Start Disks To find the program, In the search menu, enter "discs". In order to start the software, click Discs. Locate the USB Drive
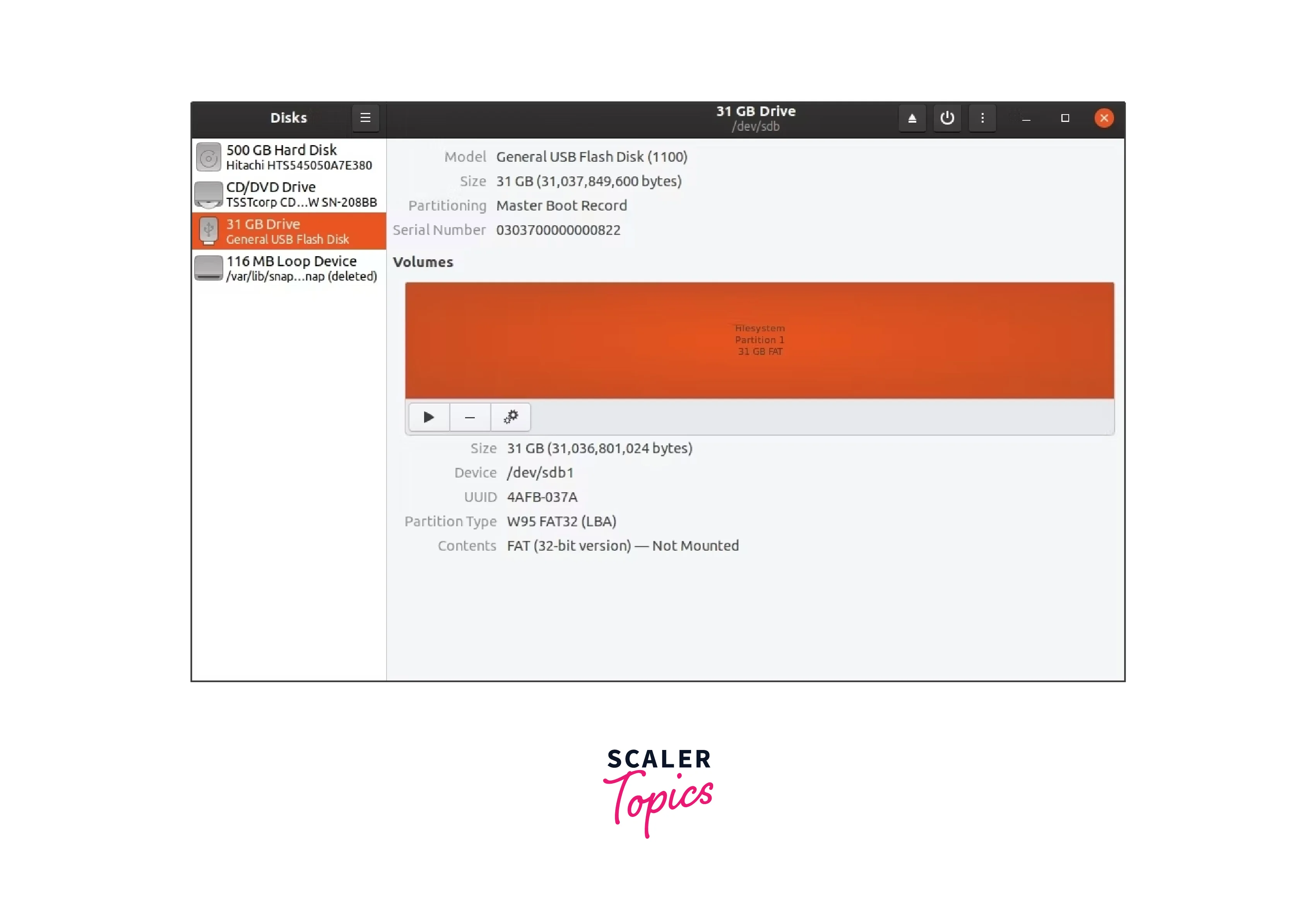 available devices by discs
A list of all available storage devices, including HDDs and USBs, will be
provided by discs. Connect your USB if you haven't previously, then look for
the drive in the list of linked devices. Click on the USB to choose it.
Format the USB Drive
After selecting the appropriate device, you can start formatting. Selecting
the Gear icon in the bottom menu will bring up the Format Partition option.
available devices by discs
A list of all available storage devices, including HDDs and USBs, will be
provided by discs. Connect your USB if you haven't previously, then look for
the drive in the list of linked devices. Click on the USB to choose it.
Format the USB Drive
After selecting the appropriate device, you can start formatting. Selecting
the Gear icon in the bottom menu will bring up the Format Partition option.
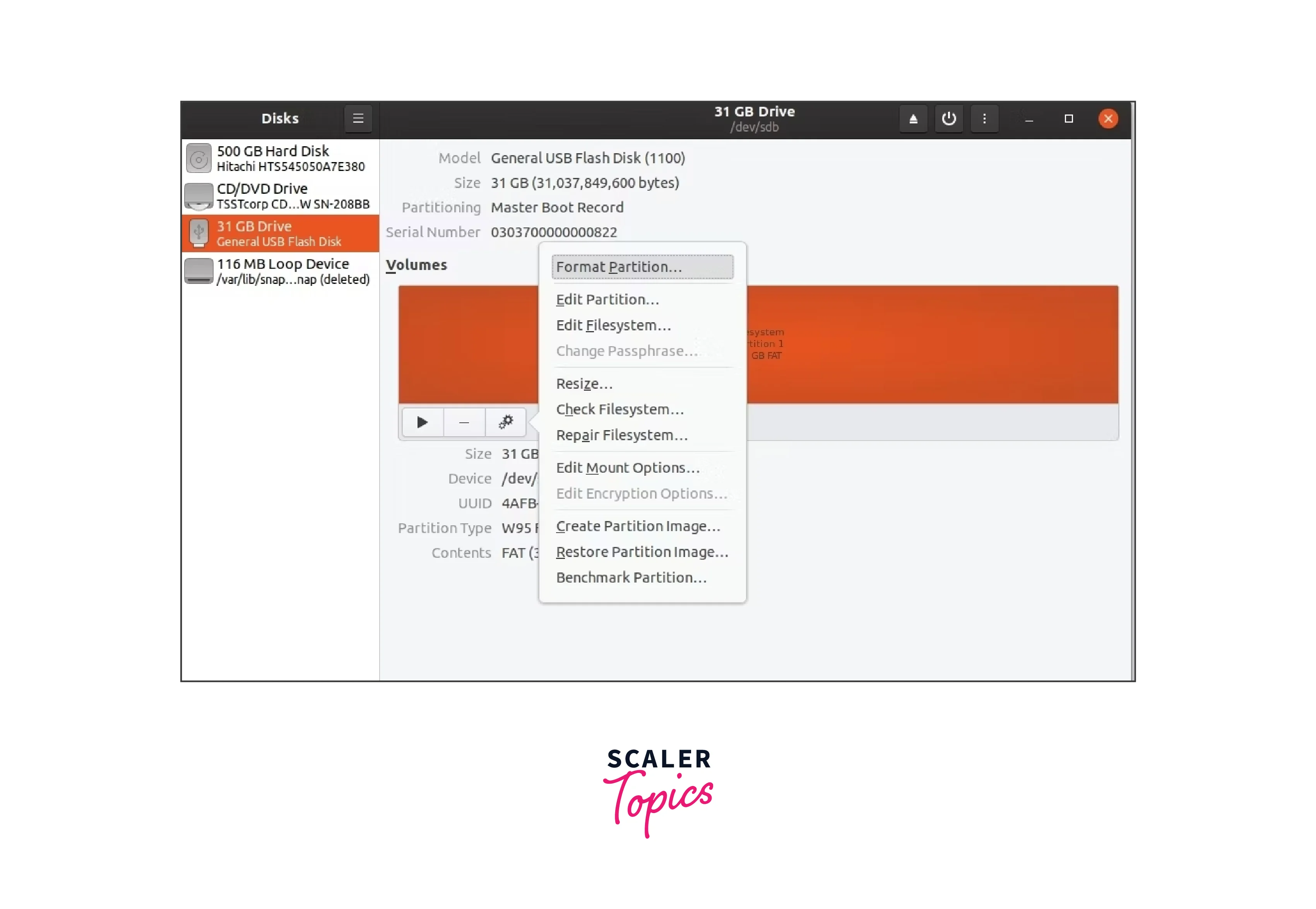 format appropriate usb drive
The dialogue box that displays allows you to name the USB drive, select the
partition type, and erase any previously saved data. The best partition type
is FAT since it works with all devices and operating systems. You can select
any alternative type if you'd like.
format appropriate usb drive
The dialogue box that displays allows you to name the USB drive, select the
partition type, and erase any previously saved data. The best partition type
is FAT since it works with all devices and operating systems. You can select
any alternative type if you'd like.
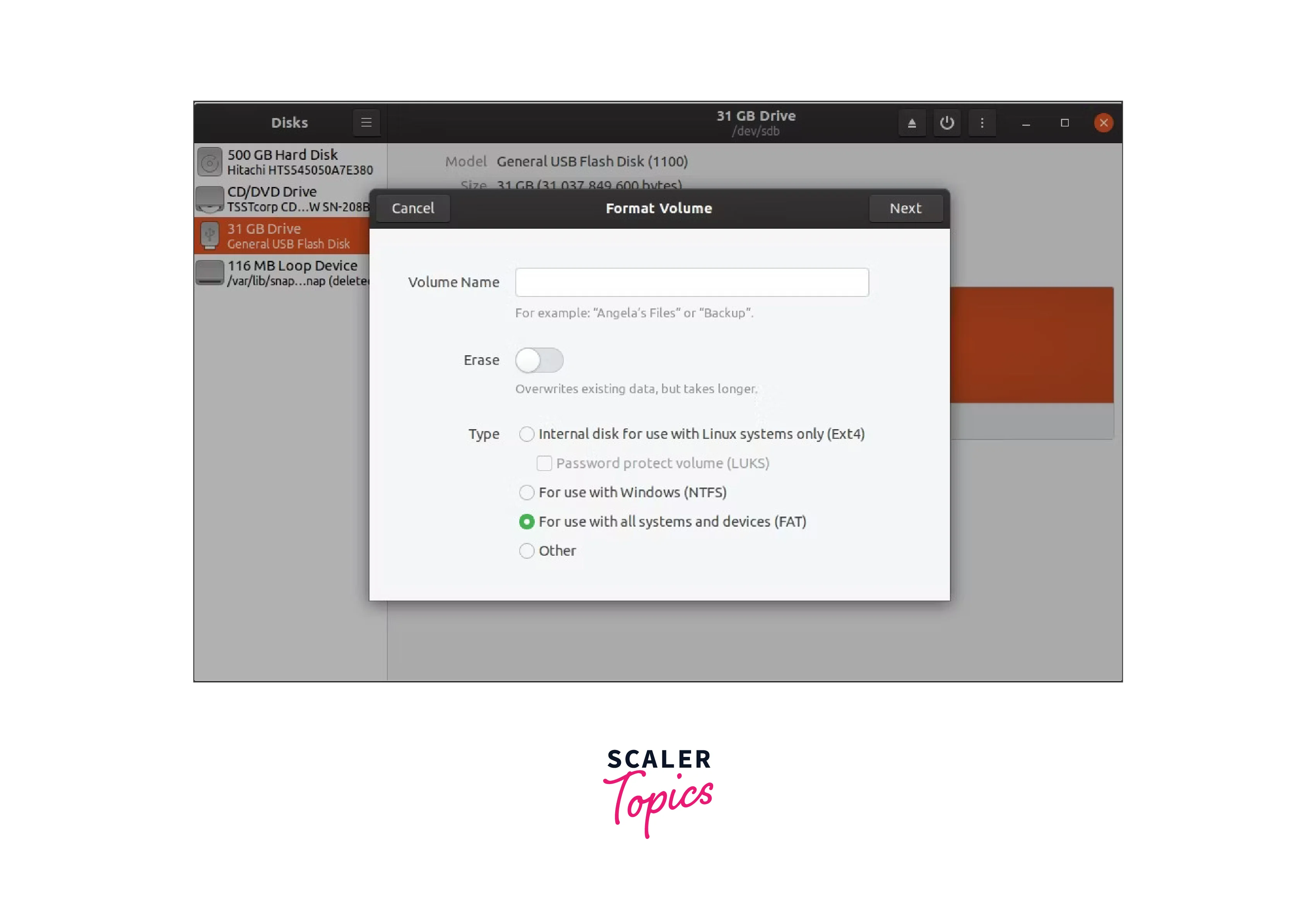 name usb drive and details
Next, move on to the prompt that displays a data loss warning by clicking
Next. To finish formatting your USB in Linux, click Format.
name usb drive and details
Next, move on to the prompt that displays a data loss warning by clicking
Next. To finish formatting your USB in Linux, click Format.
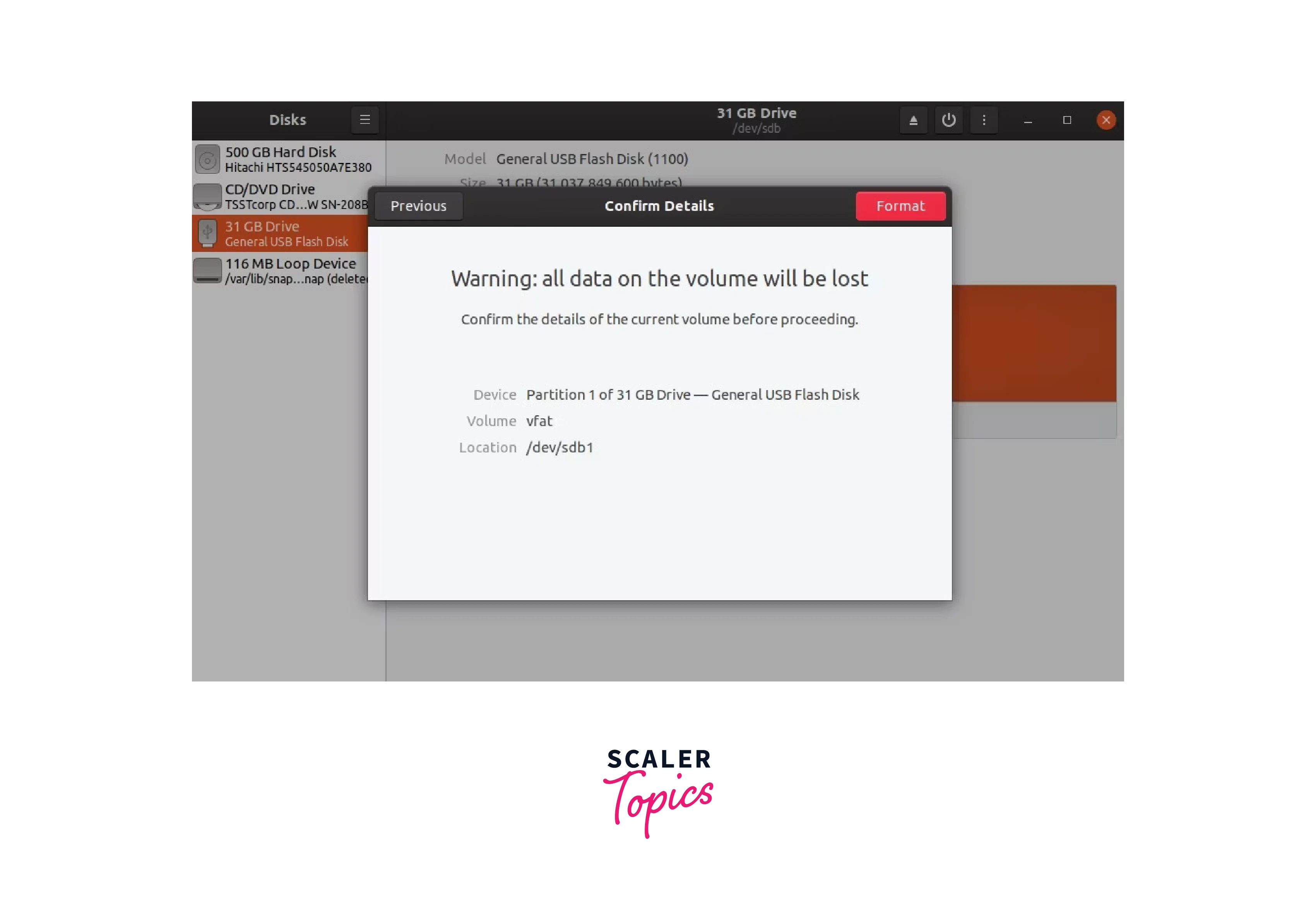 finish formatting usb in linux
You can replace Discs with the KDE Partition Manager program if you're using
KDE rather than GNOME. There shouldn't be any problems because the steps are
quite identical.
finish formatting usb in linux
You can replace Discs with the KDE Partition Manager program if you're using
KDE rather than GNOME. There shouldn't be any problems because the steps are
quite identical.
Format USB Drive Using GParted In linux format USB can also be done using GParted. GParted is a powerful disc management program that makes it simpler for Linux users to format USB devices. Utilizing one of the commands listed below, you may install it on your system: # Ubuntu and Debian sudo apt install gparted # RHEL and CentOS sudo yum install gparted # Arch Linux sudo pacman -S gparted Once GParted is installed, you may use it to format storage devices and create, resize, or delete partitions. To format your USB using GParted, carefully follow the steps listed below. Start GParted GParted can be accessed by looking for it in the dash menu. As soon as you launch the software, make sure your USB is plugged in. The initialization of the storage devices will take a little while.
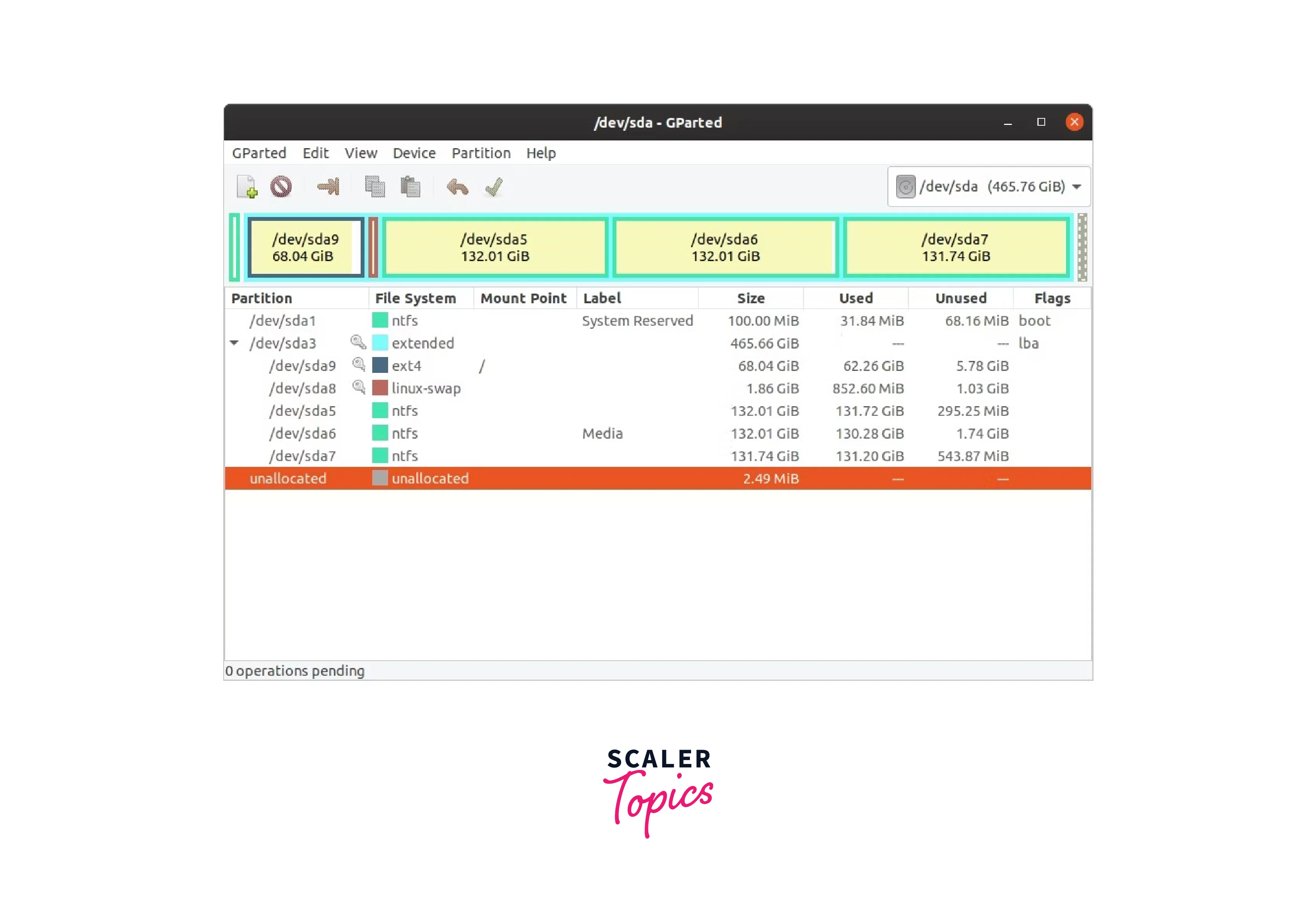 start gparted
Locate the USB Drive
You must choose your unique USB from the top-right option once it has
started. Select the desired device by clicking on the disc icon. The
/dev/sdb device utilized earlier is used in the subsequent example.
start gparted
Locate the USB Drive
You must choose your unique USB from the top-right option once it has
started. Select the desired device by clicking on the disc icon. The
/dev/sdb device utilized earlier is used in the subsequent example.
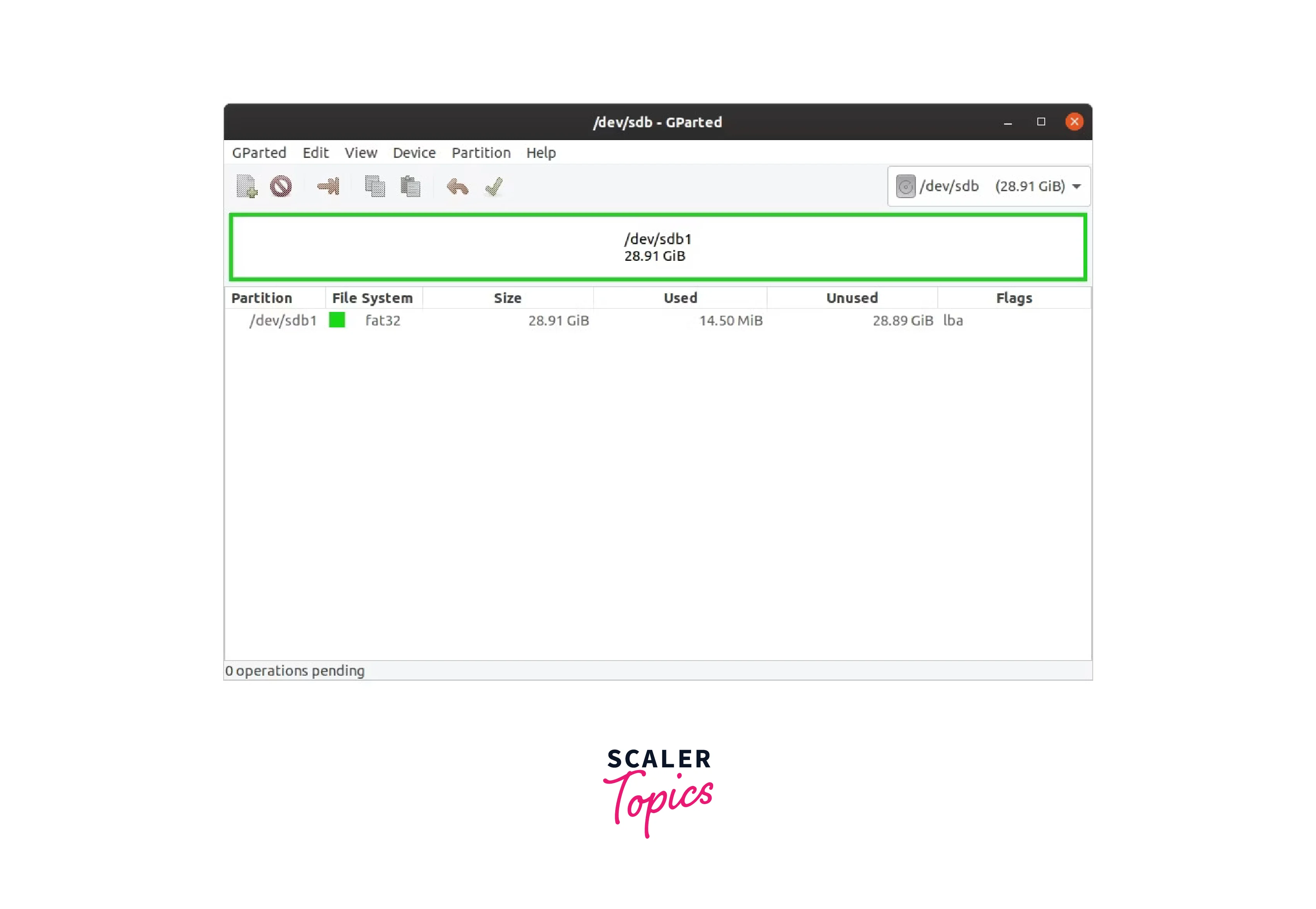 dev sdb device
Format the USB Drive
Right-click on the partition table and choose Format to after choosing the
USB drive. Select fat32 as your partition type, or any other type you
prefer. Now that GParted is open, your USB can be formatted with the chosen
file system. There will be a prompt at the bottom informing you that an
operation is about to take place.
dev sdb device
Format the USB Drive
Right-click on the partition table and choose Format to after choosing the
USB drive. Select fat32 as your partition type, or any other type you
prefer. Now that GParted is open, your USB can be formatted with the chosen
file system. There will be a prompt at the bottom informing you that an
operation is about to take place.
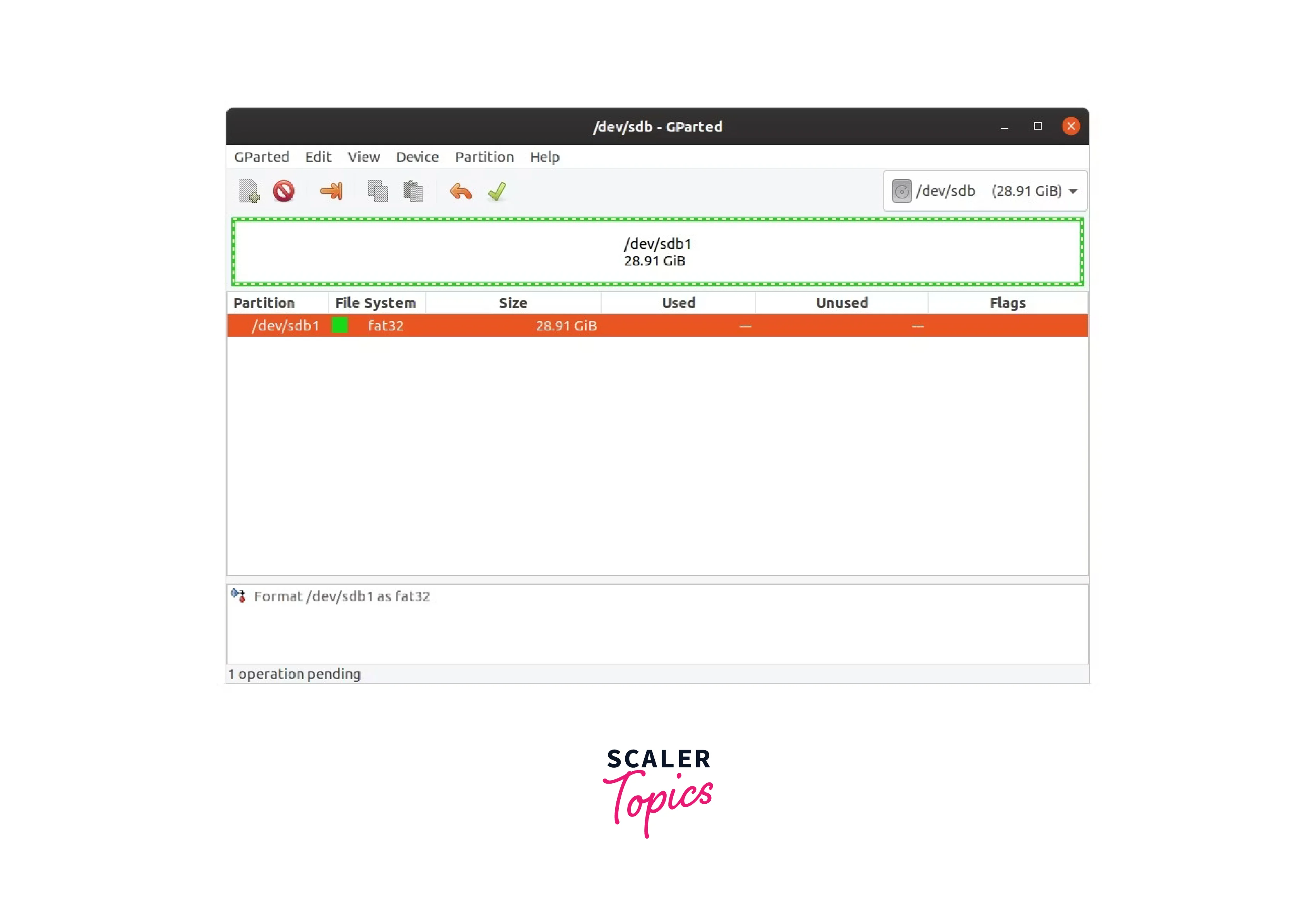 partition of usb drive
Now all you have to do is click the green checkmark icon in the top menu,
and a confirmation box will appear. For the USB to be formatted, click
Apply.
partition of usb drive
Now all you have to do is click the green checkmark icon in the top menu,
and a confirmation box will appear. For the USB to be formatted, click
Apply.
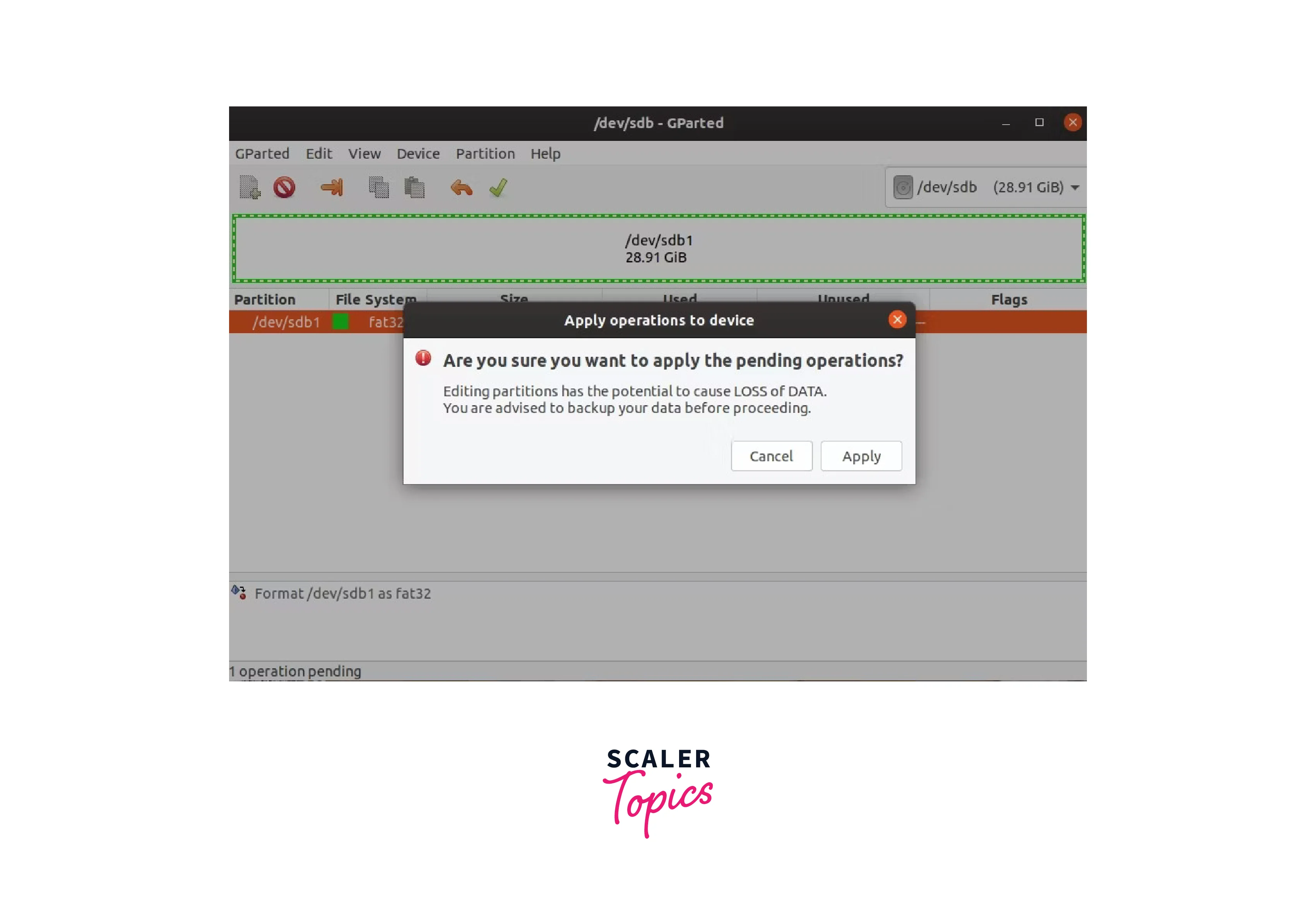 usb formatted
Your USB will be formatted in a matter of seconds. GParted will show you a
progress meter to let you know how the operation is going.
Learn More
You can follow these article too for more such operations in Linux. [link]
usb formatted
Your USB will be formatted in a matter of seconds. GParted will show you a
progress meter to let you know how the operation is going.
Learn More
You can follow these article too for more such operations in Linux. [link]
Conclusion Here's a summary of formatting a USB drive on Linux using the Terminal, Disk Utility, and GParted tool:
- Using the Terminal:
- Open a terminal window.
- Identify the USB drive's device name using the lsblk or fdisk -l command.
- Unmount the USB drive if it is currently mounted.
- Format the USB drive using a specific command for the desired file system (e.g., mkfs.fat for FAT32, mkfs.ntfs for NTFS, mkfs.ext4 for ext4).
- Using Disk Utility (GNOME Disks):
- Open the Disk Utility application.
- Select the USB drive from the list of devices.
- Click on the gear icon or select "Format Disk" from the menu.
- Choose the desired file system and provide a new name for the USB drive.
- Click "Format" to initiate the formatting process.
- Using GParted:
- Install GParted if it is not already available.
- Open GParted.
- Select the USB drive from the list of devices.
- Right-click on the USB drive and choose "Format to" or "Create Partition Table."
- Select the desired file system and apply the changes