How to Run a Script at Boot
From: https://linuxconfig.org/how-to-run-script-on-startup-on-ubuntu-22-04-jammy-jellyfish-server-desktop
How to run script on startup on Ubuntu 22.04
Jammy Jellyfish Server/Desktop 10 June 2022 by Korbin Brown
The purpose of this article is to configure a script such as a Bash script
or Python script to run upon system startup in Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish
Server/Desktop.
 How to run script on startup on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish
Server/Desktop
Software Requirements and Linux Command Line Conventions
How to run script on startup on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish
Server/Desktop
Software Requirements and Linux Command Line Conventions
| Category | Requirements, Conventions or Software Version Used
|
| System | Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish
|
| Software | N/A
|
| Other | Privileged access to your Linux system as root or via the sudo
command.
|
| Conventions | # – requires given linux commands to be executed with root
privileges either directly as a root user or by use of sudo command
$ – requires given linux commands to be executed as a regular non
-privileged user
|
How to run script on startup
on Ubuntu 22.04 step by step instructions
The Ubuntu 22.04 is based on Systemd hence the simplest and recommended way to
run a script on startup is to create a Systemd service file and execute any
script such as bash, python etc, via this service during the system boot.
The below steps will show you to run an example bash script which reports disk
space usage of the /home directory and saves the report in the /root directory
every time the Ubuntu 22.04 system boots.
Step 1 First, create a Systemd service file as in an example below. We will
store this file as /etc/systemd/system/disk-space-check.service.
[Unit]
After=network.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/disk-space-check.sh
[Install]
WantedBy=default.target
After:
Instructs systemd on when the script should be run. In our case the script
will run after network connection. Other example could be mysql.target etc.
ExecStart: This field provides a full path to the actual script to be
executed on startup
WantedBy: Into what boot target the systemd unit should be installed
NOTE
For more information on how to create Systemd service unit execute the man
systemd.unit command.
Step 2 Create a script to be executed on Ubuntu system startup. As
specified in the above Step 1, the path and the name of the new script in
our example will be /usr/local/bin/disk-space-check.sh.
The below is an example of such script:
#!/bin/bash
date > /root/disk_space_report.txt
du -sh /home/ >> /root/disk_space_report.txt
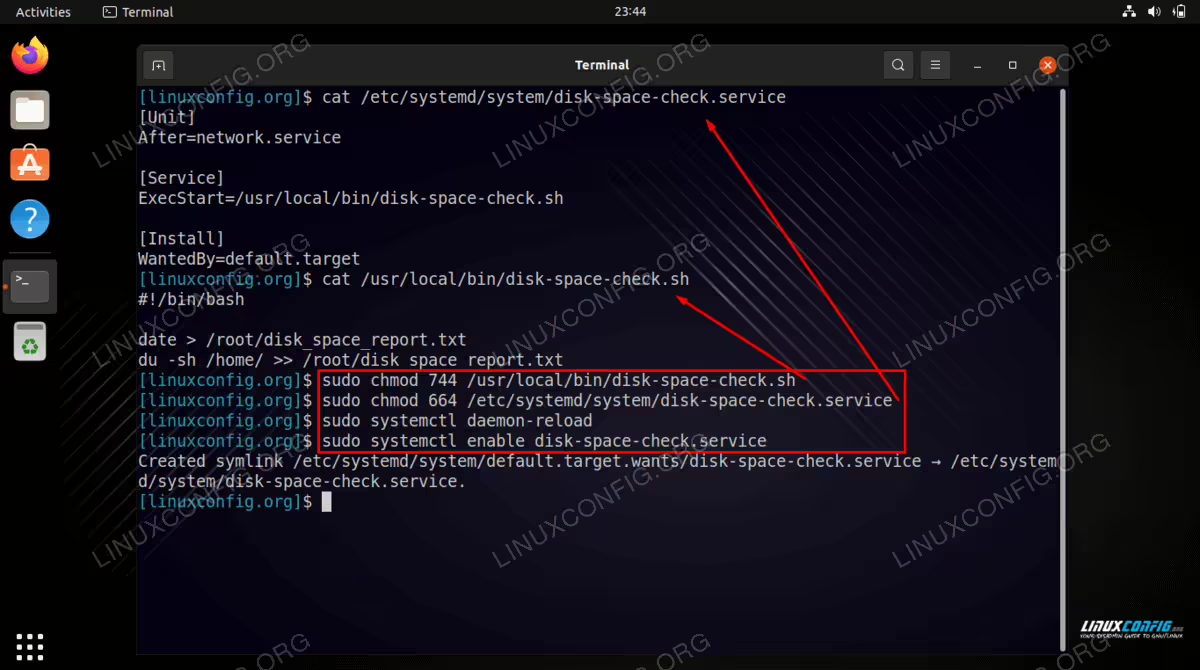
Step 3 Set appropriate permissions for both, the Systemd service unit and
script:
$ sudo chmod 744 /usr/local/bin/disk-space-check.sh
$ sudo chmod 664 /etc/systemd/system/disk-space-check.service
Step 4 Next, enable the service unit:
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
$ sudo systemctl enable disk-space-check.service
Now you are ready to reboot your system. Once the system boots you should
see the following file containing disk space usage within your /root
directory:
$ sudo ls /root/
disk_space_report.txt
Closing Thoughts
In this tutorial, we saw how to configure Ubuntu 22.04 to run a script upon
each system startup. This is a handy feature for system administrators to
implement in order to make sure a Bash or Python script is executed every
time Ubuntu loads in from a system reboot
 How to run script on startup on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish
Server/Desktop
Software Requirements and Linux Command Line Conventions
How to run script on startup on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish
Server/Desktop
Software Requirements and Linux Command Line Conventions
How to run script on startup on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish Server/Desktop Software Requirements and Linux Command Line Conventions