Getting Date & Time From NTP Server With ESP32
 ESP32 Tutorial For Reading Time & Date From NTP Server
Every now and then, you’ll come across an idea where keeping time is a top
priority. For example, consider a relay that must be activated at a specific
time or a data logger that must store values at precise intervals.
The first thing that comes to mind is to use an RTC (Real Time Clock) chip.
However, because these chips are not perfectly accurate, you must perform manual
adjustments on a regular basis to keep them synchronized.
Instead, it is preferable to employ the Network Time Protocol (NTP). If your
ESP32 project has Internet access, you can obtain date and time (with a
precision of a few milliseconds of UTC) for FREE. Also, you don’t need any
additional hardware.
ESP32 Tutorial For Reading Time & Date From NTP Server
Every now and then, you’ll come across an idea where keeping time is a top
priority. For example, consider a relay that must be activated at a specific
time or a data logger that must store values at precise intervals.
The first thing that comes to mind is to use an RTC (Real Time Clock) chip.
However, because these chips are not perfectly accurate, you must perform manual
adjustments on a regular basis to keep them synchronized.
Instead, it is preferable to employ the Network Time Protocol (NTP). If your
ESP32 project has Internet access, you can obtain date and time (with a
precision of a few milliseconds of UTC) for FREE. Also, you don’t need any
additional hardware.
What is an NTP?
NTP is an abbreviation for Network Time Protocol. It is a standard Internet
Protocol (IP) for synchronizing computer clocks over a network.
This protocol synchronizes all networked devices to Coordinated Universal Time
(UTC) within a few milliseconds ( 50 milliseconds over the public Internet and
under 5 milliseconds in a LAN environment).
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is a global time standard that is similar to
GMT (Greenwich Mean Time). UTC does not change; it is the same all over the
world.
The idea here is to use NTP to set the computer clocks to UTC and then apply any
local time zone offset or daylight saving time offset. This allows us to
synchronize our computer clocks regardless of location or time zone differences.
NTP Architecture
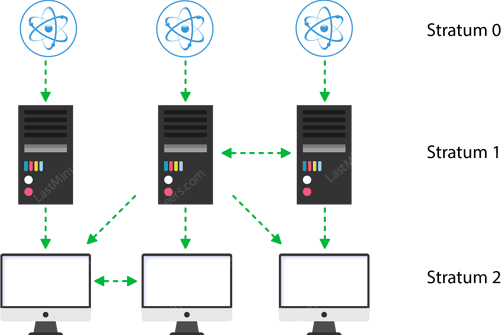
NTP employs a hierarchical architecture. Each level in the hierarchy is known
as a stratum.
 NTP Hierarchical Architecture With Stratums
At the very top are high-precision timekeeping devices, such as atomic clocks,
GPS or radio clocks, known as stratum 0 hardware clocks.
Stratum 1 servers have a direct connection to a stratum 0 hardware clock and
therefore provide the most accurate time.
Each stratum in the hierarchy synchronizes with the stratum above and acts as a
server for computers in lower stratums.
NTP Hierarchical Architecture With Stratums
At the very top are high-precision timekeeping devices, such as atomic clocks,
GPS or radio clocks, known as stratum 0 hardware clocks.
Stratum 1 servers have a direct connection to a stratum 0 hardware clock and
therefore provide the most accurate time.
Each stratum in the hierarchy synchronizes with the stratum above and acts as a
server for computers in lower stratums.
How NTP Works?
NTP can operate in a number of ways. The most common configuration is to operate
in client-server mode.
The fundamental operating principle is as follows:
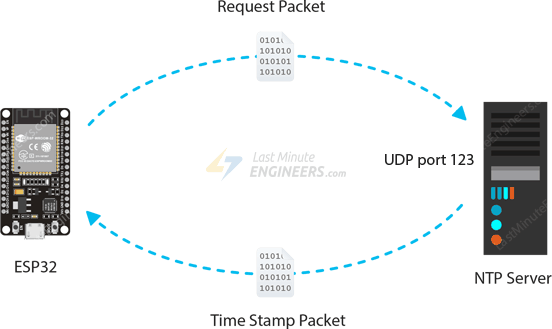
The client device, such as the ESP32, connects to the NTP server via the
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) on port 123.
The client then sends a request packet to the NTP server.
In response to this request, the NTP server sends a time stamp packet. A
time stamp packet contains a variety of data, such as a UNIX timestamp,
accuracy, delay, or timezone.
A client can then extract the current date and time from it.
 NTP Server Working - Request & Timestamp Packet Transfer
NTP Server Working - Request & Timestamp Packet Transfer
Preparing the Arduino IDE
You should have the ESP32 add-on installed in your Arduino IDE before proceeding
with this tutorial. If you haven’t installed it yet, follow the tutorial below.
Tutorial of Programming ESP32 in Arduino IDE
Insight Into ESP32 Features & Using It With Arduino IDE
Few years back, ESP8266 took the embedded IoT world by storm. For less than $3,
you could get a programmable, WiFi-enabled microcontroller being able to...
Getting Date and Time from NTP Server
The sketch below will show you exactly how to get the date and time from the
NTP Server.
Code
/*H********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
#include <WiFi.h>
#include "time.h"
//************************* DEFINES ************************************
#define BAUD 9600
const char *ssid = "YOUR_SSID";
const char *password = "YOUR_PASS";
const char *ntpServer = "pool.ntp.org";
const long gmtOffset_sec = 3600;
const int daylightOffset_sec = 3600;
//************************* PROTOTYPES ************************************
void printLocalTime();
//************************* VARIABLES ************************************
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
setup()
{
Serial.begin( BAUD );
Serial.printf( "Connecting to %s ", ssid );
WiFi.begin( ssid, password ); // CONNECT TO WiFi
while( WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED )
{
delay( 500 );
Serial.print( "." );
}
Serial.println( " CONNECTED" );
// INIT AND GET TIME
configTime( gmtOffset_sec, daylightOffset_sec, ntpServer );
printLocalTime();
// DISCONNECT WiFi AS IT'S NO LONGER NEEDEd
WiFi.disconnect( true );
WiFi.mode( WIFI_OFF );
}
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
loop()
{
delay( 1000 );
printLocalTime();
}
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
printLocalTime()
{
struct tm timeinfo;
if( !getLocalTime( &timeinfo ) )
{
Serial.println( "Failed to obtain time" );
return;
}
Serial.println( &timeinfo, "%A, %B %d %Y %H:%M:%S" );
}
Before you start uploading the sketch, you’ll need to make a few changes to make
sure it’ll work for you.
Modify the following two variables with your network credentials so that the
ESP32 can connect to an existing network.
const char* ssid = "YOUR_SSID";
const char* password = "YOUR_PASS";
Adjust the UTC offset for your timezone (in seconds). Refer to the list of
UTC time offsets. Here are some examples for various time zones:
For UTC -5.00 : -5 * 60 * 60 : -18000
For UTC +1.00 : 1 * 60 * 60 : 3600
For UTC +0.00 : 0 * 60 * 60 : 0
const long gmtOffset_sec = 3600;
Change the Daylight offset (in seconds). Set it to 3600 if your country
observes Daylight saving time; otherwise, set it to 0.
const int daylightOffset_sec = 3600;
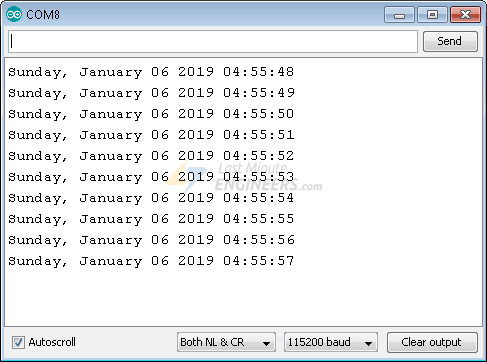
After uploading the sketch, press the EN button on your ESP32. The serial
monitor should display the date and time every second.
 ESP32 Reads Date & Time From NTP Server Output On Serial monitor
ESP32 Reads Date & Time From NTP Server Output On Serial monitor
Code Explanation
Let’s take a quick look at the code to see how it works. To begin, we include
the libraries required for this project.
WiFi.h is a library containing the ESP32-specific WiFi methods we will use
to connect to a network.
time.h is the ESP32 native time library that handles NTP server
synchronization gracefully.
#include <WiFi.h>
#include "time.h"
A few constants are then defined, such as the SSID, WiFi password, UTC offset,
and daylight offset.
const char* ssid = "YOUR_SSID";
const char* password = "YOUR_PASS";
const long gmtOffset_sec = 3600;
const int daylightOffset_sec = 3600;
In addition, the address of the NTP Server is specified. pool.ntp.org is a great
open NTP project for this kind of thing.
const char* ntpServer = "pool.ntp.org";
pool.ntp.org automatically selects time servers that are physically close to
you. However, if you want to select a specific server, use one of the
pool.ntp.org sub-zones.
| Area | HostName |
|---|---|
| Worldwide | pool.ntp.org |
| Asia | asia.pool.ntp.org |
| Europe | europe.pool.ntp.org |
| North America | north-america.pool.ntp.org |
| Oceania | oceania.pool.ntp.org |
| South America | south-america.pool.ntp.org |
Serial.begin(115200);
//connect to WiFi
Serial.printf( "Connecting to %s ", ssid );
WiFi.begin( ssid, password );
while( WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED )
{
delay( 500 );
Serial.print( "." );
}
Serial.println(" CONNECTED");
Once the ESP32 is connected to the network, we use the configTime() function to
initialize the NTP client and obtain the date and time from the NTP server.
//init and get the time
configTime(gmtOffset_sec, daylightOffset_sec, ntpServer);
Finally, we use the custom function printLocalTime() to print the current date
and time.
The printLocalTime() function calls the getLocalTime() function internally. The
getLocalTime() function sends a request packet to an NTP server, parses the time
stamp packet received, and stores the date and time information in a time
structure called timeinfo.
/*F********************************************************************
*
**********************************************************************/
void
printLocalTime()
{
struct tm timeinfo;
if( !getLocalTime( &timeinfo ) )
{
Serial.println( "Failed to obtain time");
return;
}
Serial.println( &timeinfo, "%A, %B %d %Y %H:%M:%S");
}
In the table below, you can see how each member of this time structure relates
to a certain piece of information.
| %A | returns day of week |
| %B | returns month of year |
| %d | returns day of month |
| %Y | returns year |
| %H | returns hour |
| %M | returns minutes |
| %S | returns seconds |